What is Smart Contract in Blockchain?
Smart Contracts are integral part of blockchain. They happen to be a piece of logic which deals within the blockchain blocks. Lets see some official definition too
“A Smart Contract (or cryptocontract) is a computer program that directly and automatically controls the transfer of digital assets between the parties under certain conditions.”
So precisely speaking smart contracts work similar to normal legal contracts that work offline however the smart contracts become “smart” in nature as they work for the technology world.
Let’s look at some default types of smart contracts:
Smart Contracts Types:
1. Smart legal contract:
So the smart contracts are guaranteed by law. The business rules of law can be converted into a contract which makes it a smart legal contract.
The parties involved execute contracts with digital signatures. Smart legal contracts may be executed autonomously if certain prerequisites are fulfilled, for example, making a payment when a specific deadline is reached. In the event of failure to comply, stakeholders could face severe legal repercussions.
2. Decentralized autonomous organizations:
In DAOs, No executive or president exists. So the organizations still exists however they become autonomous and decentralized in nature.
3. Application logic contracts:
The application specific contracts are supposedly mapped to application logic contracts. So think of an example in IOT, where the devices are connected to each other. The communication of those devices is being done via block chain and the contracts written for the communication between them will be application logic contracts.
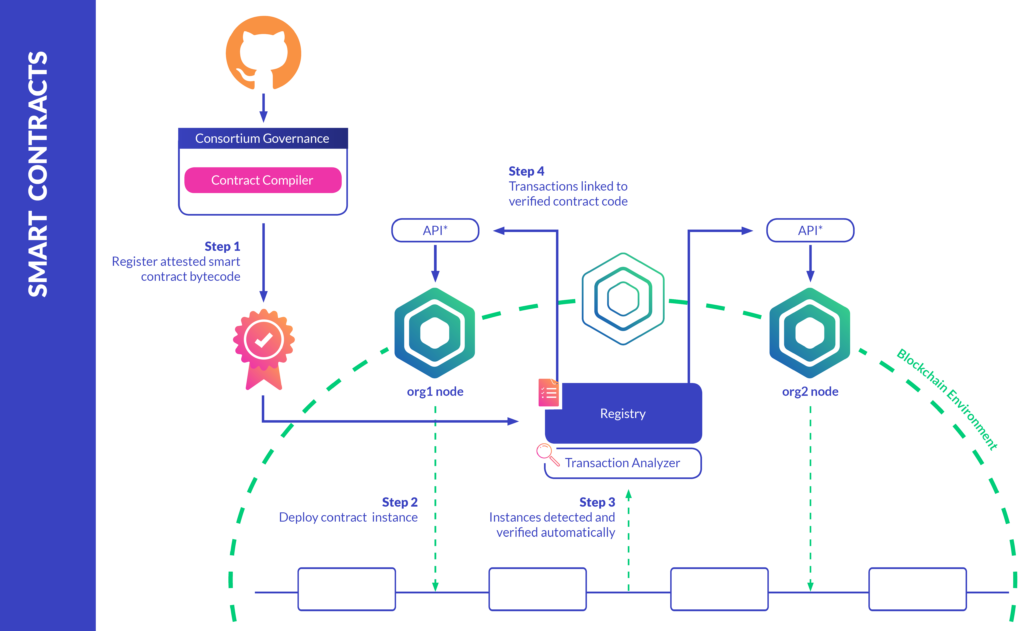
Now lets look at some use cases of Application Logic Contracts or we can say were smart contracts are useful:
- Royalty payment in media and entertainment
Media industry is quite benefited in the terms of Royalty payments as the originality is preserved from the artist side. - Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications
Financial Transactions in the Blockchain space have been the most favoured in terms of the application of it. Smart Contracts running on these block chains help maintain Ledger in a transparent fashion. - Conversion of assets into non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
Non Fungible tokens aka NFTs have been a very recent phenomenon where in the Tokens shared on the network on the Blockchain. And the smart contracts which help in creating the NFTs regulate the circulation in the network. - B2B data marketplaces
A data marketplace is a portal where users can buy and sell diverse datasets or data streams from a wide range of sources. Intelligent contracts facilitate the creation of dynamic and fast-evolving markets that support automated and secure transactions without the hassle of human intervention. Datapace is a good example of this particular smart contract use case. - Supply chain management
In the domain of supply chain management, blockchains are actively utilized to make the management more autonomous. Consider an organization which has created smart contracts for the entire supply chain and they are without mediators. By this the management wont require auditing. And during the supply of the goods if there is any delay in shipments then escalation will happen automatically via the smart contracts. - Digital identity cards
Considering the immutable nature of blockchain, the smart contracts written on the top of the blockchain can help in creating digital identity cards which can store the information long term and be accurate in it. The kind of data stored in can be a reputational data something like individual credit scores. - Electoral polls.
Elections in any region, state or country are a politically sensitive events. Thus the collection of electoral polls and storing then in a secure and immutable way needs to be done. One of the property which is immutability in block chain helps achieving this for designing Electoral polls with smart contracts.
Now lets us look at some challenges that smart contract technology still faces despite plethora of use cases ( since the grass can’t stay always green )
The first and foremost challenge that we see with smart contracts is the regulation. The international community has not come up with some standard benchmarking or we can say regulations for smart contracts. Regulations make the governance of the contract little easier ( however if we regulate more than required then it really becomes a mess ).
The second challenge that we see is in the difficulty of implementation of the contracts. Every developer of blockchain inherently understands the nuances for this challenge. The toolkit available in the developer world for implementing smart contracts is still in its nascent stage and requires more contribution from the community.
The third challenge that the smart contract technology still faces is the alignment with the network in which it executes. The shared understanding of the network for making smart contracts work is really important.
Thus on concluding remarks we can say that the world of smart contract has been ever changing and developing in terms of challenges, limitations and learning for developers.
What to read more about Blockchain ? Check our blog, where you can find more about Blockchain and Crypto.

