Introduction to Polkadot Cryptocurrency:
Cryptocurrencies have always been in the market of all the happening reasons. Polkadot shines for is uniqueness around the chaos for currencies. Yes! Polkadot is pretty unique in nature. So What does Polkadot bring to the table of these mammoth blockchain technologies. Well we can get into the origins of Polkadot first.
History of Polkadot:
Polkadot was first launched by Dr. Gavin Wood. Dr. Gavin wood was already a part of Ethereum blockchain inception. By being the part of the founder team of Ethereum he is well aware of the Pros and Cons of Ethereum. In 2017, when Polkadot was first released it had the first glance of the blockchain space where it introduced a novel idea of relay chain. Polkadot was built by Parity Technologies.
So what’s under the hood of Polkadot?
Being from the Decentralized world of Block chains, Polkadots also uses decentralized protocol to transfer funds from one digital wallet to another.
But beware as Polkadot is not just limited to authorizing transactions, it can do a lot more than that.
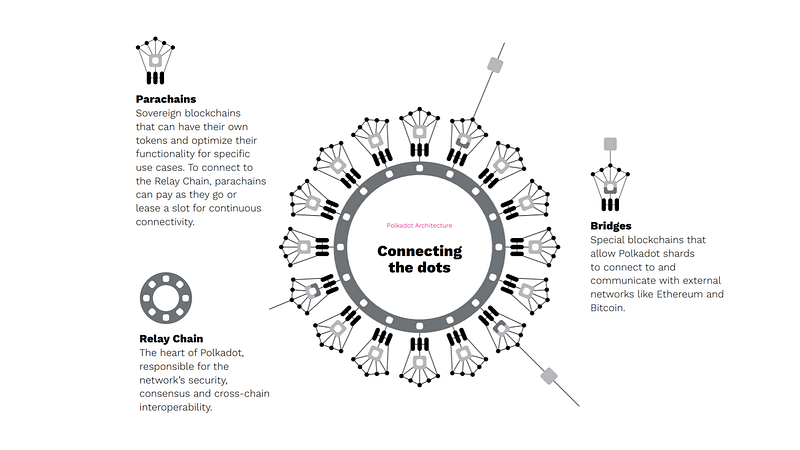
This network allows the creation of three types of blockchains including
- Relay Chain
- Parachain
- Bridges
These three words might make us wonder what they might be exactly, so why not have a look at them individually..
Lets first look at Relay chain in Polkadot:
So Relaychain happens to be the most important part of this Polkadots technology. Relaychain helps in processing data and transactions on several chains in parallel which are also known as Parachains.
Secondly we have parachains in Polkadot:
As the name goes they are along side the relay chains and help relay chains in verifying the accuracy of transactions.. Thus parachains help in reducing the high fees, maintaining the congestion and incompatibility of legacy blockchains and they help improve interoperability, scalability and cross chain functionality.
Thirdly we have bridges in Polkadot:
Polkadot uses these protocols to interact with other blockchains. The developers are currently working on building bridges with Ethereum, Cosmos, Bitcoin, and EOS. Using this method, Polkadot will allow users to swap tokens without using a centralized exchange.
Polkadot Working:
Considering all these technologies in mind the last point stays with the security of the data ingrained in Polkadots…
Here Polkadots follows shared security model.
But how does shared security approach work ?
In Polkadot, shared security is achieved through a mechanism called “Nominated Proof-of-Stake” (NPoS) and the relay chain structure.
- Relay Chain Security:
- Polkadot has a relay chain at its core, which acts as the main chain connecting and securing all parachains (individual blockchains that connect to the relay chain).
- The relay chain provides security to all connected parachains by maintaining a shared security model. This means that the security of each parachain is not isolated but benefits from the collective security of the entire network.
- Validators and Nominators:
- Validators are nodes in the Polkadot network responsible for producing new blocks on the relay chain and securing the overall network.
- Nominators are participants who lock their DOT tokens to support validators. By doing so, they contribute to the security of the network and receive a share of the rewards earned by the validators they nominate.
- Dynamic Validator Set:
- Polkadot’s NPoS consensus mechanism allows for a dynamic set of validators. Token holders can nominate validators, and those with the highest total backing (nominations plus their own stake) become part of the active validator set.
- This dynamic selection process promotes decentralization and responsiveness to changes in the network’s security requirements.
- Slashable Offenses:
- Validators and nominators are subject to “slashing” penalties for malicious behavior or downtime. This ensures that participants have a vested interest in maintaining the security and integrity of the network.
Polkadot GRANDPA Protocol:

In making Polkadot crypto work there is one fascinating protocol called GRANDPA protocol.
The fullform of GRANDPA is GRANDPA (GHOST-based Recursive ANcestor Deriving Prefix Agreement).
The Polkadot Host uses the GRANDPA Finality protocol to finalize blocks. Finality is obtained by consecutive rounds of voting by the validator nodes. Validators execute GRANDPA finality process in parallel to Block Production as an independent service.
Challenges and considerations:
- Competition: Polkadot faces competition from other Layer 1 and Layer 2 blockchain solutions, each vying for dominance in the Web3 space. Continued innovation and development will be crucial to maintain its competitive edge.
- Complexity: Polkadot’s technical architecture can be intricate for newcomers, potentially hindering wider adoption. User-friendly tools and educational resources are essential to bridge this gap and attract a broader audience.
- Security vulnerabilities: As with any blockchain technology, Polkadot is not immune to security risks. Ongoing security audits and proactive measures are necessary to maintain user trust and confidence.
Read More: What is Chainlink?